Detailed guide on taxes in Greece
In Greece, income tax for individuals may reach 44%, but new tax residents can qualify for special tax regimes and lessen their tax burden. Corporate income is taxed at 22%. Greek tax rates are the same for tax residents and non-residents.

On the features of the Greek taxation system

Who pays taxes in Greece?
In Greece, taxes are paid by individuals and businesses. Taxes are imposed on income, movable and immovable property, capital gains, added value, gifts and inheritance, dividends, interest, royalties, etc.
In case of gainful employment, both employer and employee pay social security contributions. High-net-worth individuals and companies with large turnovers are also subject to different taxes on “luxury”.
In general, Greek tax rates do not depend on tax residence. Greek taxes for non-residents coincide with those for residents but some exceptions. For example, Greek tax resident companies are exempt from tax on royalties, while non-Greek resident businesses pay it at 20%.
An individual is considered a Greek tax resident if they spend more than 183 days per annum in Greece. Suppose a person spends 183 days neither in Greece nor any other country. In that case, other grounds like ownership of assets, citizenship, social security registration, and the country where the family reside, and children go to school are taken into consideration.
A legal entity is considered a Greek tax resident if it has been incorporated or established according to the Greek legislation, has its registered seat in Greece, or the place of its effective management is located in Greece.
The Greek financial year coincides with the calendar year and follows the year of income. It starts on January 1st and ends on December 31st. If legal entities keep double entry books, the taxable period may end on June 30th. The tax return must be submitted by the last day of the sixth month from the end of the tax year, which generally is June 30th.
Greek taxes for individuals
Individual income tax is levied according to three different progressive scales. Employment income, business profits and pensions are taxed from 9 to 44%. Rental income is taxed from 15 to 45%. All income is additionally taxed from 0 to 10% for solidarity contribution.
Residents are taxed on their worldwide income, while non-Greek residents are taxed only on Greek-source income.
In case of gainful employment, employers transmit income taxes to the tax authorities every month, and employees do not need to declare such income.
Individual income tax rates
Let us make a sample calculation. For example, till the end of the tax year, a Greek taxpayer earned €40,000: €25,000 at work and €15,000 for renting out an apartment.
For employment income, this individual will pay 9% of €10,000, 22% of another €10,000 and 28% of €5,000, which makes up €4,500. For rental income, they will pay 15% of €12,000 and 35% of €3,000, which make up €2,850. As a solidarity contribution, they will pay 6,5% of €40,000, or €2,600. In total, their income is taxed at €9,950.
Property taxes. When you buy a property in Greece, you pay real estate transfer tax, or FMA, at 3,09% of the property value. Then, you annually pay a uniform tax on the ownership of real estate property, or ENFIA, and a municipal tax, or TAP.
The municipal tax is levied at 0.025—0.035% of the real estate’s value, depending on the property location and age, and included in the utility bills. The uniform tax depends not only on the objective value of the property but on its size, location, surface, use, zone price, age, etc. as well, so it is calculated individually.
How to pay property taxes in Greece:
Before the purchase, the buyer files the property transfer tax return, which can be done online through the myPROPERTY, and pays the resulting tax.
After the purchase, the owner files the property data statement, or E9 form, through the myAADE. It must be done within 30 days from the date the purchase and sale agreement was signed. To obtain a username and a password for myAADE, the owner registers with the Taxisnet e-services.
Based on information from the E9 form, The Independent Authority for Public Revenue, or AADE, calculates the amount of ENFIA, issues an administrative tax assessment and notifies the owner via email. Then, ENFIA’s tax notices are published yearly on the myAADE platform.
The property owner logs into the myAADE website, selects “Debts, Payments and Contributions” (“Οφειλές, πληρωμές & επιστροφές”) from the menu, and sees the amount to be paid, the dates of the instalments and the debt identifier required to make a payment to the bank.
The owner pays the tax via online banking or in a bank’s branch in person.
Other taxes for individuals like social security contribution, capital gain tax, taxes on dividends, interest and royalties are usually levied at a flat rate. Though, tax on inheritance is imposed according to the progressive scale depending on the relationship between the inherited person and the heir.
These taxes are levied at the following rates:
capital gain at 15%;
social security contribution at 14,12% of salary;
withholding tax on dividends at 5%;
withholding tax on interest at 15%;
withholding tax on royalties at 20%, and royalties paid to Greece resident corporations are exempt from taxation;
inheritance at up to 10% for close relatives and up to 40% for the rest of the heirs;
gifts to close relatives at 10%, while gifts of less than €800,000 value are exempt from tax. Gifts to other people — at up to 40%.

For a stay in the 5-star Grande Bretagne hotel in Athens, guests have to pay €4 as the stayover tax. This tax was implemented in 2018 and is levied at €0.25—4, depending on hotel categories
Preferential tax regimes in Greece
Income taxes in Greece for foreigners can be reduced if they become tax residents of Greece and switch to one of the three special tax regimes.
The regime for foreigners employed in Greece can be applied to those new greek tax residents who work in Greek companies, are self-employed or operate a business in Greece. Under this regime, 50% of income earned in Greece is exempt from tax for seven years.
An individual is eligible for this regime if they:
Were not Greek tax residents for 5 out of 6 previous years.
Have transferred their tax residence from a country with which Greece has an agreement for administrative cooperation in tax matters.
Are employed in a Greek company or operate a business in Greece.
Have declared their intention to stay in Greece for at least two years.
The foreign pensioners’ regime is an alternative taxation regime for retirees who have recently become Greek tax residents. Under this regime, their foreign income is taxed at a flat rate of 7%, which must be paid in lump sum until the last business day of July. This tax treatment is also applied for a maximum of 15 years.
7%
Foreign source income tax rate for retirees
A retiree is eligible to join this regime if they were not Greek tax residents for 5 out of 6 previous years and if their last tax residence was a country with which Greece has in force an agreement for administrative cooperation in tax matters.
Under the foreign pensioners’ regime, retirees must report both their Greek and foreign source income in tax returns.
The high-net-worth individual regime, or HNWI, is an alternative way of taxation on foreign source income earned by individuals who have recently become Greek tax residents. Under the HNWI regime, individuals pay a lump tax of €100,000 per year, regardless of their income. They are also exempt from inheritance and gift tax on their foreign assets. The regime may be applied for up to 15 years.
A person is eligible for this tax treatment if they were not Greek tax residents for 7 out of 8 previous years. To switch to the HNWI regime, an applicant must invest €500,000 in real estate, moveable assets or shares of legal entities based in Greece or within the framework of the Greece Golden Visa program.
An investor’s relatives may join them and need to pay an additional €20,000 per annum.
If investors or their relatives who pay taxes under the HNWI regime earn income in Greece, it is taxed and must be reported in the tax return. Besides, any tax they paid abroad is not offset against Greek tax liabilities.
The application deadline is March 31st for any of the three tax regimes described above. The application will be considered within 60 days.
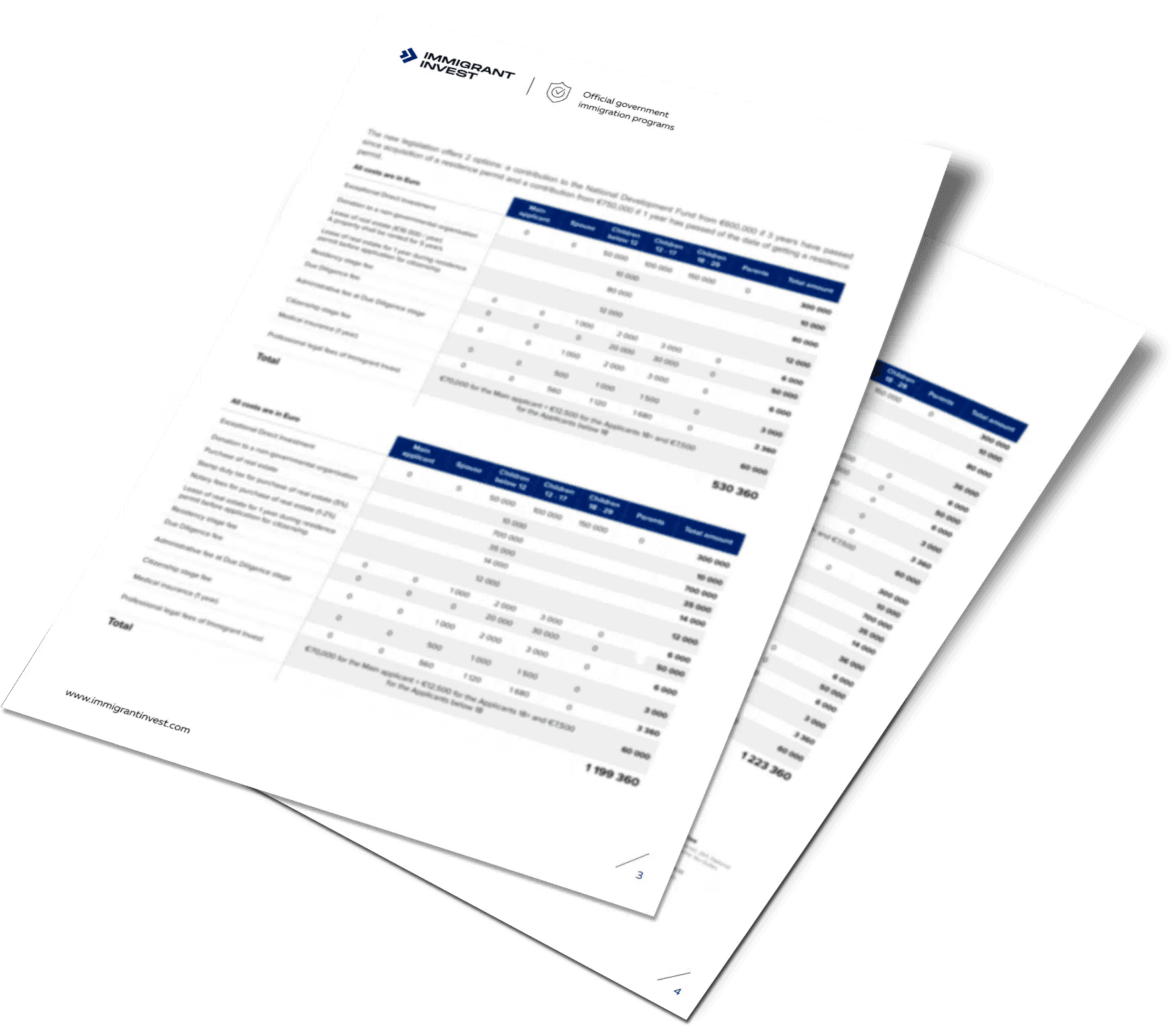
Individual cost calculation of the residence permit in Greece
Greek taxes for businesses
Corporate income tax in Greece is levied at a flat rate of 22%, which was reduced from 24% in 2021. The exception is credit institutions: their profit is taxed at 29%. Capital gains are treated as regular business income.
22%
The corporate income tax rate in Greece
Resident companies are taxed on their worldwide profit, while non-Greek resident entities are taxed only on the profit earned in Greece. The country also imposes income tax on Controlled Foreign Companies (CFCs) profits. A CFC is a non-Greek company whose controlling stake is owned by a tax resident of Greece.
Value-added tax, or VAT, applies to almost all goods and services in Greece. The standard rate is 24%, but it can be reduced due to the location or the type of a good or service. On the five Greek islands, VAT rates are reduced by 30%. Small enterprises that have supplied goods and provided services of no more than €10,000 per annum can join the special regime and be exempted from paying VAT.
VAT rates in Greece
The luxury tax is imposed on goods like jewellery, clothing and footwear made of fur or leather. The rate is 10%. Aeroplanes, seaplanes and helicopters for private use are subject to 20% luxury tax.
Property ownership tax, or ENFIA, is calculated similarly to the tax for individuals. However, companies are subject to a supplementary tax of 0,55% of their property rights. If the real estate is used for the production or performance of any business activity, the supplementary tax rate is 0,1%.
Some companies that own properties are subject to a special tax on real estate or SRET. It is charged annually at 15% of the objective real estate’s value, but some categories of businesses are exempt from this tax, according to Article 15 of Law 3091/2002.
Other taxes:
social security contribution is paid by employers at 22,54% of salary;
excise tax reaches 35% on tobacco and 63,7% on fuel;
withholding tax rates coincide with the rates for individuals: 5% for dividends, 15% for interest and 20% for royalties. If a company meets certain conditions, it may be exempt from paying withholding taxes.

The town of Preveza is a tourist hub with many clubs, bars and cafes. In Greece, beer is pretty expensive, as the excise tax on beer is among the highest in the EU: €0.21 per 330ml bottle. Yet, wine and sparkling wine are exempt from excise tax in Greece
Double tax treaties that Greece has signed
Greece has signed Double Tax Treaties with 57 countries, among which are all the EU states, India and China.
In most cases, treatments apply to income and capital. But Germany, Italy, Spain and the USA have extended agreements with Greece that apply to real estate, inheritances and gifts as well.
Countries that Greece has signed double tax treaties
Albania,
Armenia,
Austria,
Azerbaijan,
Belgium,
Bosnia-Herzegovina,
Bulgaria,
Canada,
China,
Croatia,
Cyprus,
Czech Republic,
Denmark,
Egypt,
Estonia,
Finland,
France,
Georgia,
Germany,
Hungary,
Iceland,
India,
Ireland,
Israel,
Italy,
Kuwait,
Latvia,
Lithuania,
Luxembourg,
Morocco,
Mexico,
Malta,
Moldavia,
Netherlands,
Norway,
Poland,
Portugal,
Qatar,
Romania,
Russia,
Saudi Arabia,
San Marino,
Serbia,
Slovakia,
Slovenia,
South Africa,
South Korea,
Sweden,
Spain,
Switzerland,
Turkey,
Tunisia,
Ukraine,
United Arab Emirates,
United Kingdom,
United States,
Uzbekistan.
How to get Greece residency to become a Greek tax resident
Usual Schengen visas do not allow spending more than 180 days a year in Greece, and foreigners need to spend at least 183 days there to qualify as tax residents. It becomes possible if they get a Greek residence permit.
There are several ways to obtain residency in Greece: enter a Greek university, get a job in a Greek company or marry a citizen of Greece. Wealthy foreigners apply for a residence permit for financially independent persons or a Greece Golden Visa.
Residence permits for financially independent persons are issued to those applicants who earn at least €2,000 per month and have at least €24,000 on their account in a Greek bank. Residence cards are valid for two years and then have to be renewed.
Golden Visas are issued to those applicants who have invested at least €250,000 in the Greek economy. The minimum amount applies to real estate options: purchase of a property or land, 10-year rent or timeshare. If applicants purchase securities or open a deposit, they must invest a minimum of €400,000. Residence cards are valid for five years.
Greece Golden Visa investment options
€250,000+ — real estate purchase or rent;
land purchase€400,000+ — purchase of securities; opening a bank deposit
In the Greek residence permit by investment application, the investor can include their spouse, unmarried children under 21 and parents. Investors themselves must be over 18, have no criminal record and be able to prove the legality of their income.
The application is processed within 1—2 months, and the procedure of the Greece Golden Visa obtainment takes about half a year.
To pay taxes in Greece, foreigners need to get a taxpayer identification number. In the Greek language, it is called an AFM. One can obtain it from the local Tax Office or Internal Revenue Services, either in the place of residence or in the area where the person is buying property.
An AFM can be applied in person or through a power of attorney. The required documents are an ID card and proof of address. If a non-Greek tax resident needs to get an AFM, they must appoint a tax representative in Greece.
Upon receiving the AFM number, its holder must submit the E1 tax return form annually, even if they did not reside in Greece during the assessment year and earned no income in the country. Property owners additionally submit the E9 form every year.
Immigrant Invest is a licensed agent for citizenship and residence by investment programs in the EU, the Caribbean, Asia, and the Middle East. Take advantage of our global 15-year expertise — schedule a meeting with our investment programs experts.

Practical Guide
Will you obtain a residence permit in Greece?
Frequently asked questions
Case studies

How we won the court against the Portuguese migration service regarding no decision on residency

Malta citizenship for a Taiwanese family so that their children get prestige education

Greece Golden Visa: how an Israeli family prepared a plan B in Europe













